Carbon Resistors:
 A component whose function in a circuit is to provide a specified value of resistance is called a carbon resistor. A carbon resistor is manufactured by baking a powdered carbon mixed with a binding material. This results in a small tube with a wire attached to both ends. The range of carbon resistor is from a fraction of an ohm to several million ohms. The power rating of a carbon resistor depends upon the physical size of the resistor. Power rating means the electrical by consumed by a component or converted into another form of energy by that component. In our case resistor is going to be discussed so a large resistor is able to dissipate more energy into heat than a smaller one which means larger resistor consumes more power and that is why its power rating is high.
Color coding scheme:
A component whose function in a circuit is to provide a specified value of resistance is called a carbon resistor. A carbon resistor is manufactured by baking a powdered carbon mixed with a binding material. This results in a small tube with a wire attached to both ends. The range of carbon resistor is from a fraction of an ohm to several million ohms. The power rating of a carbon resistor depends upon the physical size of the resistor. Power rating means the electrical by consumed by a component or converted into another form of energy by that component. In our case resistor is going to be discussed so a large resistor is able to dissipate more energy into heat than a smaller one which means larger resistor consumes more power and that is why its power rating is high.
Color coding scheme:
A color code is printed on a carbon resistor which gives us information about the resistance of that resistor. In this scheme generally a carbon resistor has four bands of color as A, B, C and D on it. They are used to determine the resistance of a particular carbon resistor. First band on the carbon resistor gives us first digit and the second one provides us with second digit. Third band is a decimal multiplier. It means our third band gives us number of zeros. Fourth band stands for tolerance. Tolerance is a specified percentage which is added or subtracted from the value formed by the color bands A, B, and C.
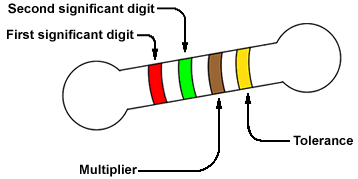
Tolerance band is provided because due to manufacturing variations, the resistance value may not be same as indicated by the color code printed on the carbon resistor. It provides a limit to the user within which a carbon resistor can have its actual value of resistance.
Color code for resistance value Color code for tolerance
Black 0 Green 5 Gold ± 5 %
Brown 1 Blue 6 Silver ± 10 %
Red 2 Violet 7 No Color ± 20 %
Orange 3 Gray 8
Yellow 4 White 9
Example:
Suppose we have a carbon resistor printed with color bands as A=brown, B=Black, C=Red and D=Silver then the resistor of resistance will be calculated from the table above as
R=10×000±10% Ω
On simplification
R=10 kΩ±10%
It means the resistance of resistor lies between 9000 Ω and 11000 Ω.

A color code is printed on a carbon resistor which gives us information about the resistance of that resistor. In this scheme generally a carbon resistor has four bands of color as A, B, C and D on it. They are used to determine the resistance of a particular carbon resistor. First band on the carbon resistor gives us first digit and the second one provides us with second digit. Third band is a decimal multiplier. It means our third band gives us number of zeros. Fourth band stands for tolerance. Tolerance is a specified percentage which is added or subtracted from the value formed by the color bands A, B, and C.

Tolerance band is provided because due to manufacturing variations, the resistance value may not be same as indicated by the color code printed on the carbon resistor. It provides a limit to the user within which a carbon resistor can have its actual value of resistance.
Comments
Post a Comment