Well if you are going to study Electrical Engineering first you will have to study Physics which is "Mother of Electrical Engineering". In addition to this you should be good at basic mathematics too but don't worry here we will explain each and everything in detail. So let's start.
Basic Concept:
First of all we would try to understand what is matter because this field starts from matter. For this I would like to give you a clear and concise overview with a latest theory in this field called modern electron theory of matter.
Modern Electron Theory of Matter:
This theory describes that all matter whether solid , liquid , gas and plasma is composed of small particles called molecules and a molecule is made up of atoms.Further an atom has two parts nucleus which is the central part of atom. Nucleus contains protons and neutrons mainly. The charge on the proton is positive and its magnitude is 1.602×10−19 C and the other particle is neutron which is neutral i.e it has zero electric charge. While the mass of proton is just equal to the mass of neutron. Due to this reason most of the mass is found in the nucleus. The surrounding part which is also called extra-nucleus contains electron revolving around the nucleus in different paths called orbits. Electrons are negatively charged particles with same magnitude as proton but with different mass which is less than that of proton.

Matter is called Electrical naturally, Why?
Yes matter is electrical in nature because it contains particles of electricity viz electrons and protons .
We will show here two cases about electrical nature of matter.
Case 1:
Atom under normal conditions is neutral as whole. It means the net charge on the atom is zero because number of electrons under normal conditions is equal to the number of protons. In a such case matter will not conduct electricity. Its simplest example is the page of a book.
Case 2:
If we have neutral body and we add electrons to it or remove from, certainly it will will be having some charge.Now the body is ready to conduct electricity. It means the body should have either less or more electrons as compared to protons but not equal.
Free electrons:
As we know electrons revolve around the nucleus in different orbits and an atom can have many orbits depending upon its atomic number. The electrons in the last orbit of an atom are called valence electrons.In case of metals these valence electrons are very weakly attached to to their nuclei and are called free electrons.The concept of electric current can be understood by these electrons.One may note that all valence electrons are not free electrons but only those valence electrons can be regarded as free electrons that can leave their parent atom under slightest applications used for removal.It should also be noted that one atom can provide at the most one free electron.
Electric Current:
It is very easy to understand electric current.The word "Current" means flow.Now we are going to define electric current as
"The flow of free electrons or charges in a definite direction is called electric current."It is defined in this way too
" Rate of change of electric charges."
Current is represented by I and it is given by the relation as below
I= dq/dt
Unit:
The unit of electric current in SI system is ampere represented by A and is defined as coulomb per second.
Direction of Current:
The current is a scalar quantity no matter we are going to discuss its direction. This is because of it does not obey law of parallelogram which must be obeyed by vectors.Conventionally , the direction of electric current is taken along the motion of positive charges but one should keeping in mind that positive charges never move they are only electrons which moves and cause current.The direction which is taken along the motion of actual.
Electric Potential:
Electric potential is a very important concept in electrical engineering. It is analogous to pressure. Just as pressure exerted a force on the water to flow in a certain direction, the same is done by electric potential in case of electric charges to bring them to movement. In electrical engineering electric potential which is also called electromotive force or simply e.m.f is defined as
"Electric potential or e.m.f of a body is the work done done in joules to bring a unit positive charge from infinity to that body."
It means if a unit positive charge is lying at an infinite distance from a body and work is done on that unit positive charge to bring it near to the body then there will be developed a force or potential in the brought up charge and is called electromotive force.
We all know very well when we raised a body from the ground at some height it develops gravitational potential energy in it and has ability to do work when released. In the very same way when a body is provided with charges from outside then it will develop electric potential energy which has also ability when its charges are allowed to move free.
In above both case both cases some work is done on the respective bodies and that work is stored in the form of energy in them. From the above explanation we can define electric potential in a very simplest way as
"Work done per unit charge is called electric potential or e.m.f ."
It is represent by V.
Mathematically,
V= W/Q
Unit:
The unit of electric potential is volt and is defined as
"The electric potential of a body is one volt when one joule of work is done on a unit positive charge to bring it from infinity to that body."
Potential Difference:
The two terms electric potential (E.m.f) and potential difference looks like same but there is a large difference between the two. It will be explained very well in the following analogy.
Consider we have two tanks filled by water and joined by a pipe and they are placed at a well leveled surface.What does it mean? It means both tanks are at same pressure and as both are filled so no water flow will occur. The same is true when two bodies are at same potential and no charges will flow resulting in zero current.But what will happen if we outflow water from one of the tanks above.Will water move to the other tank? No because the two tanks are placed on a leveled surface.In order to move water to the other tank we will have to do some work on the first tank and that will develop a difference between the pressures of two tanks and causes the water to flow to the second tank.This is the same story with potential difference.It means when two charged bodies having different potentials are joined by a conductor current will start flowing.We can conclude from above as
"Difference in potentials of two charged bodies is called potential difference."
The following example also explains concept of potential
difference very well.Suppose we have two bodies as Body
A = + 5 V and Body B = +3 V.The difference in potentials is given as
Potential difference=Potential on body A-Potential on body B= 5 V- 3 V= 2 V.
We know that when a body loses electrons it will get positive charge. It means the body A is more deficient of electrons as it has more positive charge as compared to body B. Now if we join body A with body B by means of some conductor then electrons will start flowing from body A to body B.After some time both bodies will be at same potential i.e +4 V and the electrons’ flow will be ceased. it is interesting that the unit of potential difference is also volt. As current is the flow of charges it means if there is potential difference there will be current but we have seen from above example that potential will be leveled after some specific time and current will be zero as flow of charges has stopped. In order to maintain potential difference what we need is called battery which is said to have e.m.f. here we conclude that
“Potential difference causes current to flow while e.m.f maintains potential difference.”



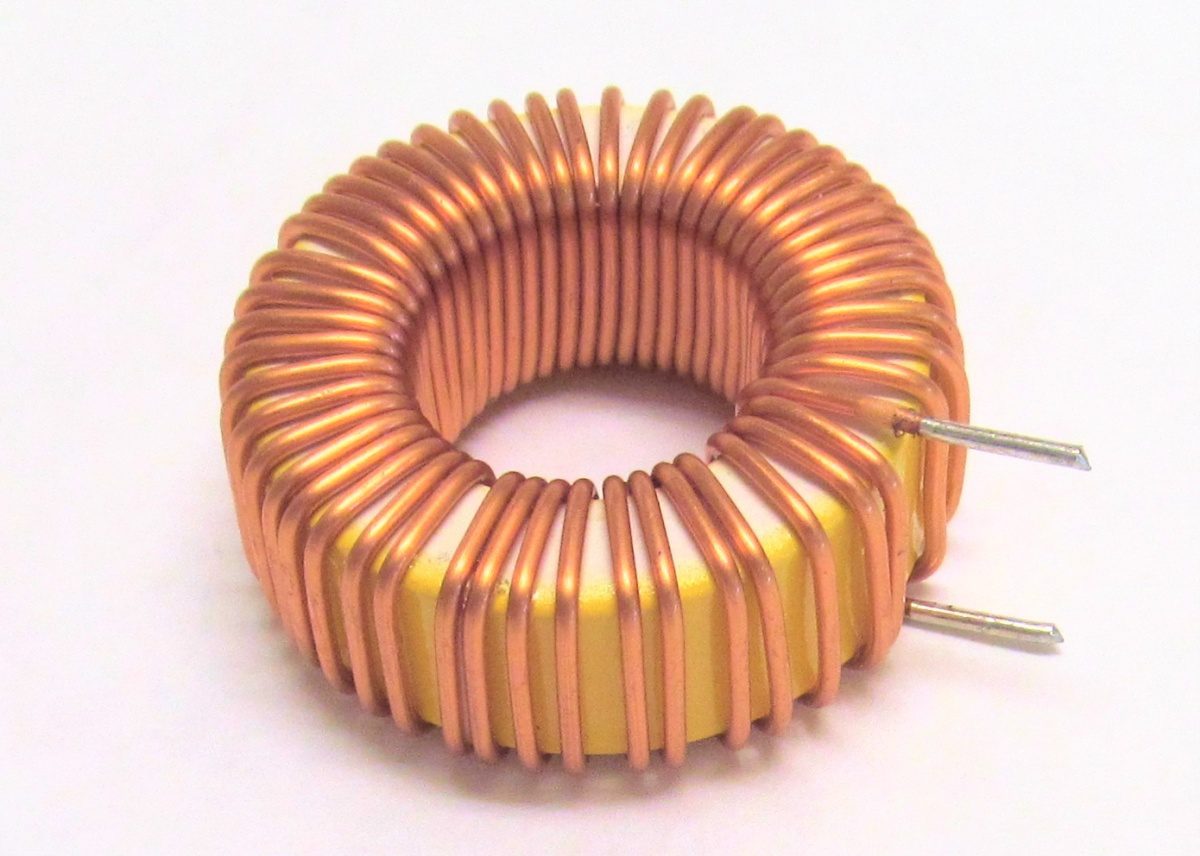
Inductor
An electrical element which is used to store energy in the form of magnetic field is called inductor. It is made or manufactured by giving turns in the form of a loop to a simple wire. The resulting product is simply called a coil which when subjected to electricity stores energy and is called inductor. The property of inductor which tells us how much energy it can store is called its inductance.The symbol for inductor is as given in following

Potential difference=Potential on body A-Potential on body B= 5 V- 3 V= 2 V.
We know that when a body loses electrons it will get positive charge. It means the body A is more deficient of electrons as it has more positive charge as compared to body B. Now if we join body A with body B by means of some conductor then electrons will start flowing from body A to body B.After some time both bodies will be at same potential i.e +4 V and the electrons’ flow will be ceased. it is interesting that the unit of potential difference is also volt. As current is the flow of charges it means if there is potential difference there will be current but we have seen from above example that potential will be leveled after some specific time and current will be zero as flow of charges has stopped. In order to maintain potential difference what we need is called battery which is said to have e.m.f. here we conclude that
“Potential difference causes current to flow while e.m.f maintains potential difference.”
Resistor
It is defined as an electrical element which is used to confine or limit electric current through it. The property by which it opposes the flow of current is called resistance. One should remember that every electrical element has some resistance.The symbol for resistor is given below asCapacitor
An electrical element which is used to store energy in the form of electric field is called capacitor. It mainly contains two plates. One is positively charged and the other is negatively charged with an insulating material called dielectric in between them. The property of capacitor which tells us how much energy it can store is called capacitance.The symbols for capacitors are shown below as
Inductor
An electrical element which is used to store energy in the form of magnetic field is called inductor. It is made or manufactured by giving turns in the form of a loop to a simple wire. The resulting product is simply called a coil which when subjected to electricity stores energy and is called inductor. The property of inductor which tells us how much energy it can store is called its inductance.The symbol for inductor is as given in following

Electrical Power:
Power is simply defined as work done per unit time.The same definition is exactly true in case of electrical engineering too. The relation for mechanical power is given as
P=W/t ..........(a)
We have defined electric current and potential difference in the beginning as I=q/t and V=W/q respectively.
From current formula
q=It .......(1)
and from potential difference given above
W=qV .......(2)
Putting value of q from (1) in (2)
W=ItV
putting this value in eq (a)
P=ItV/t
P=IV
This is the general formula for electrical power.

Comments
Post a Comment